01 Coagulation

- occurs before any thrombus formation

- coagulation = fibrin formation into clot to stop blood loss
Coagulation Factors

- First soluble. Become insoluble when activated



Coagulation Cascade
Main

- fibrin insoluble, precipitate


Tissue Factor

- when endothelium intact, no contact
- when damaged, tissue factors expressed


- not very effective, no amplification
Thrombin

- thrombin amplification
- 5, 8, 11 activate more 10


Von Willebrand

- unique: in endothelium
- megakaryocytes: von willebrand stored in platelets and endothelium
- injury: factor 8 released from vWF, thrombin formation
Factor 13

- formed but not crosslinked

Factor 12

- activate coagulation system when exposed to silica
Extrinsic and Intrinsic

- how written in textbook
- 1st pathway: TF pathway from TF:VIIa
- 2nd pathway: factor 12
- T: which factors activated by thrombin




- phospholipid: required, exists on TF cells or platelets
Calcium


- used to be called factor 4

Kinin

- contact pathway: activated when plasma in contact with negatively charged substances
- link between coagulation and inflammation
- generated by factor 12


- factor 12 leads to synthesis of bradykinin
- link between coagulation system and kinin system (inflammation)
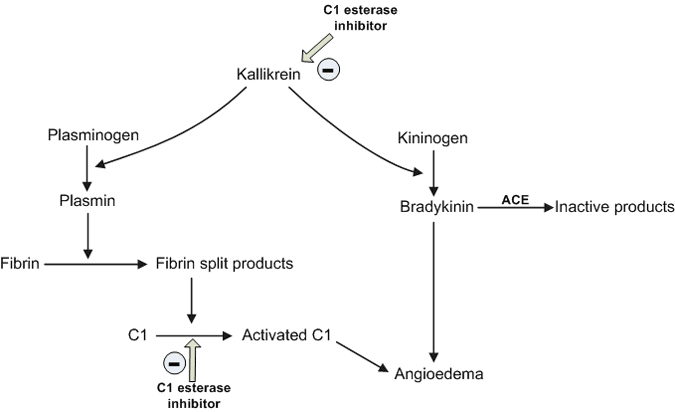

- cannot activate bradykinin
- routine test of PTT shows prolonged. No medical problems because 12 doesn't have a lot of physiologic significance

Coagulation Inhibitors

Antithrombin III

- activated by healthy endothelial cells
Protein C and S


- healthy endothelium: produce lots of thrombomodulin, less thrombin

- deficiency in one or both: hypercoagulable
- factor 5 leiden mutation: cannot be inactivated by protein C/S: hypercoagulable

- just know plasma level increased with heparin
- Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (or TFPI) is a single-chain polypeptide which can reversibly inhibit Factor Xa (Xa). While Xa is inhibited, the Xa-TFPI complex can subsequently also inhibit the FVIIa-tissue factor complex. TFPI contributes significantly to the inhibition of Xa in vivo, despite being present at concentrations of only 2.5 nM.
Plaminogen

- break down fibrin
- converted to active in plasma




- contain crosslinked bond by 13
- indicates crosslinked fibrin clot broken down

- FDP can increase without clot formation: not useful

- break down of fibrinogen but not clot
- break down other clotting factors: deplete clotting factors
- looks like DIC
- increased in prostate cancer and cirrhosis
- alpha2- antiplasmin inhibitor of plasmin. Loss can leads to overactivation

Vitamin K

ESR

- inflammation: increased protein levels
- proteins are sticky, clump RBCs together, settle faster to bottom faster

- liver makes more fibrinogen that will increase ESR
Backlinks

















































